• Isotonic : the solution in which the concentration of solutes are equal
• Hypertonic : the solution with a higher solute concentration (concentrated)
• Hypotonic : the solution with a lower solute concentration (dilute)
 | |
Example SOME RELEVANT FACTS • The Red blood cell are isotonic to 0.85% @ 0.15 M of sodium chloride (or 0.28% M glucose solution). The biconcave shape is maintained. |
• Cell sap of onion cells are isotonic to 0.5 M @ 17% sucrose solution. Cells remain turgid.
• - Isotonic solution is a solution in which the concentration of solutes is equal to that of cytoplasmic of the animal cell @ cell sap of the plant cell.
- water diffuse into and out of the cell at equal rates.
- there is no net movement of water across the plasma membrane ( no net gain @ loss of water)
- the cell retain their normal shape.
ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS IN ISOTONIC SOLUTION
- cytoplasm contains water, solute and other substances.
- contain cytoplasmic fluid that is surrounded by interstitial fluid.
- Hence, the cells are constantly subjected to osmosis.
• Plant cells :
The plants cell in isotonic solution
normal shape is retain
- water, solute and other substances are stored in vacuole (cell sap).
- The cell wall is fully permeable to solutes and water
- Hence the cells are constantly subjected to osmosis.
HYPOTONIC SOLUTION
• Hypotonic solution : a solutions which contain a higher concentration of water compared to cytoplasm @ cell sap (contain a lower concentration of solute).
• So, there is a net movement of water from outside into the cell.
ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS IN HYPOTONIC SOLUTION
HYPERTONIC SOLUTION
Hypertonic solution: a solutions which contain a higher concentration of solute compared to cytoplasm @ cell sap (contain a lower concentration of water).
• So, there is a net movement of water from inside into the outside of the cell.
ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS IN HYPERTONIC SOLUTION
THE EFFECT OF SOLUTION AT DIFFERENT CONCENTRATION ON ANIMAL AND PLANT CELL
Type of solution | Type of cell | Process | Appearance of the cells |
Hypotonic | Animal cell | Haemolysis | Haemolysed |
Plant cell | - | Turgid | |
| Hypertonic | Animal cell | Crenation | Crenated |
| Plant cell | Plasmolysis | Flaccid |
STRUCTURE OF PLASMA MEMBRANE
Phospholipids Bilayer |
The picture above show a structure of phospholipids bilayer. This structure can be found on the plasma membrane. The components of this structures are:
1. Phospholipids
2. Protein
3. Chloesterol
Phospholipids
The structure of phospholipids consists of :
1. Hydrophilic Head - love water molecule
2. Hydrophobic Tail - hate water molecule
Stucture of Phospholipids |
Protein
There are two proteins:
1. Carrier protein
2. Pore protein
Example of substances that can pass through into :
1. Carries protein - Large water molecule [ Glucose and Amino Acids]
2. Pore protein - Small water molecule [ Ions]
Cholesterol
Makes the bilayer stronger, more flexible and
less permeable to water-soluble substances such as ions
Resources: Biology Text Book Form 5
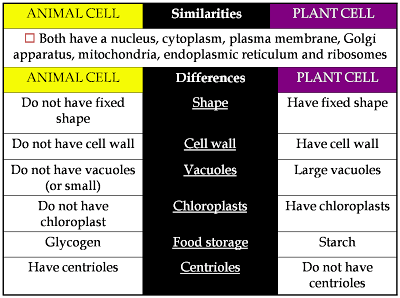
ANIMAL CELL |
PLANT CELL |
Comparison between plant cell and animal cell |














No comments:
Post a Comment